Tablespace Management :
-->A tablespace is logical group of datafiles in a database.
-->A database is divided into one or more logical storage units called "Tablespace"
-->A tablespace must have atleast one datafile in a file system which is located physically.
Server --> Oracle version --> database --> Tablespace --> Datafiles
->when a existing datafile in a tablespace completely filled up then add a extra datafile or extend the existing datafile
Oracle Database stores data logically in tablespaces and physically in datafiles associated with the corresponding tablespace.
-->A tablespace must have atleast one datafile in a file system which is located physically.
Server --> Oracle version --> database --> Tablespace --> Datafiles
->when a existing datafile in a tablespace completely filled up then add a extra datafile or extend the existing datafile
Oracle Database stores data logically in tablespaces and physically in datafiles associated with the corresponding tablespace.
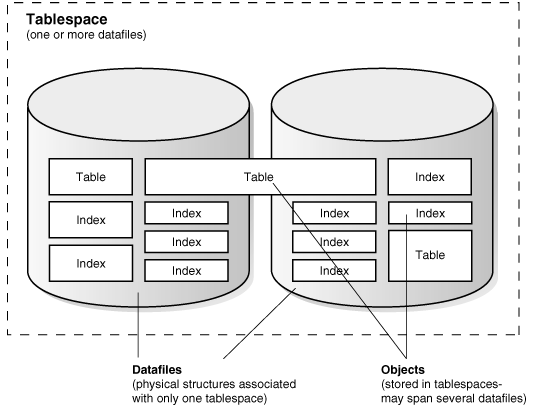
Datafiles and Tablespaces
-
An Oracle database consists of at least two logical storage units
called tablespaces, which collectively store all of the database's data.
You must have the
SYSTEMandSYSAUXtablespaces and a third tablespace, calledTEMP, is optional.
-
Each tablespace in an Oracle database consists of one or more files
called datafiles, which are physical structures that conform to the
operating system in which Oracle Database is running.
-
A database's data is collectively stored in the datafiles that
constitute each tablespace of the database. For example, the simplest
Oracle database would have one tablespace and one datafile. Another
database can have three tablespaces, each consisting of two datafiles
(for a total of six datafiles).
Oracle-Managed Files:
Oracle-managed files eliminate the need for you, the DBA, to directly manage the operating system files comprising an Oracle database. You specify operations in terms of database objects rather than filenames. Oracle Database internally uses standard file system interfaces to create and delete files as needed for the following database structures:-
Tablespaces
-
Redo log files
-
Control files
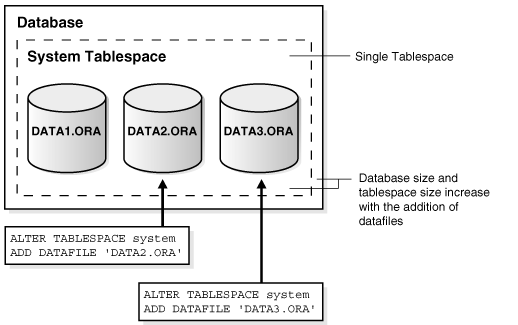
Allocate More Space for a Database:
The size of a tablespace is the size of the datafiles that constitute
the tablespace. The size of a database is the collective size of the
tablespaces that constitute the database.
You can enlarge a database in three ways:-
Add a datafile to a tablespace
-
Add a new tablespace
-
Increase the size of a datafile
Enlarging a Database by Adding a Datafile to a Tablespace
==>Alternatively, you can create a new tablespace (which contains at least one additional datafile) to increase the size of a database
Enlarging a Database by Adding a New Tablespace
 The third option for enlarging a database is to change a datafile's size
or let datafiles in existing tablespaces grow dynamically as more space
is needed. You accomplish this by altering existing files or by adding
files with dynamic extension properties
The third option for enlarging a database is to change a datafile's size
or let datafiles in existing tablespaces grow dynamically as more space
is needed. You accomplish this by altering existing files or by adding
files with dynamic extension properties -->when a create a tablespace by default it is
ONLINE ,READ WRITE, loging =yes ,pluggedin =no, permanent
-->we can transport the tablespace(introduced in oracle 8i) from one database to another database
-->we cannot drop the tablespace which holds the data, still we can drop the table space
which holds data by command
sys>>drop tablespace <tablespace name> including contents;
->Based on content we are having permanent,Temporary, and undo tablespace
->The number of dataspace we required in database depends on the number of application
that we support
->depending on storage we have two tablespaces
BIG FILE-- can have multiple datafile (default) size can grow upto 128TB
SAMLL FILE -- can have the only datafile --1024 datafiles can have in small file dataspace
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sys>>select name from v$datafile
sys>>select name from v$controlfile
sys>>select member from v$logfile
sys>>create tablespace ts1 datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf' size 100m;
sys>>desc dba_tablespaces
sys>>select tablespace_name from dba_tablespaces;
sys>>select tablespace_name,status,contents,logging,plugged_in,BIGFILE from dba_tables;
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enlarging a Database by Adding a Datafile to a Tablespace
sys>> alter tablespace ts1 add datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts2.dbf' size 4m;
sys>> select filename,tablespace_name from dba_data_files;
sys>> desc dba_data_files
sys>>select filename,tablespace_name,bytes/1024/1024 from dba_data_files;
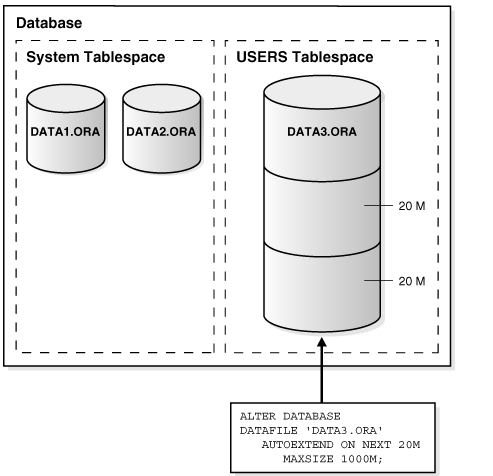
Enlarging a Database by Dynamically Sizing Datafiles
sys>> alter database datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf' resize 10m;
Enlarging a Database by automatically when the datafile get filled
sys>> alter database datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf' autoextend on maxsize 10m;
Enlarging a Database by Adding a New Tablespace
How to drop a datafile
sys>> alter tablespace drop datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf'
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Practicals for tablespace management :
To check the datafile pathsys>>select name from v$datafile
sys>>select name from v$controlfile
sys>>select member from v$logfile
Creating tablespace
sys>>create tablespace ts1 datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf' size 100m;
sys>>desc dba_tablespaces
sys>>select tablespace_name from dba_tablespaces;
sys>>select tablespace_name,status,contents,logging,plugged_in,BIGFILE from dba_tables;
To make tablespace OFFLINE
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 Offline;
To make tablespace READONLY
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 readonly;
To make tablespace READ WRITE;
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 read write;
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 Offline;
To make tablespace READONLY
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 readonly;
To make tablespace READ WRITE;
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 read write;
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enlarging a Database by Adding a Datafile to a Tablespace
sys>> alter tablespace ts1 add datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts2.dbf' size 4m;
sys>> select filename,tablespace_name from dba_data_files;
sys>> desc dba_data_files
sys>>select filename,tablespace_name,bytes/1024/1024 from dba_data_files;
Enlarging a Database by Dynamically Sizing Datafiles
sys>> alter database datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf' resize 10m;
Enlarging a Database by automatically when the datafile get filled
sys>> alter database datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf' autoextend on maxsize 10m;
Enlarging a Database by Adding a New Tablespace
sys>>create tablespace users datafile ' /disk1/oradata/ORCL/users1.dbf ' size 4m;
How to drop a datafile
sys>> alter tablespace drop datafile '/disk1/oradata/ORCL/ts1.dbf'
Rename the tablespace
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 rename to ts2;
Rename the datafile
sys>>ALTER TABLESPACE ts2
RENAME DATAFILE '/u02/oracle/rbdb1/user1.dbf',
'/u02/oracle/rbdb1/user2.dbf'
TO '/u02/oracle/rbdb1/users01.dbf',
'/u02/oracle/rbdb1/users02.dbf';
To make the default tablespace for a datafile
sys>> alter database default tablespace ts2;
sys>>select * from database_properties;
sys>>alter dabase default temporary tablespace temp1;
Rename a temporary tablespace:
sys>>alter tablespace temp1 rename to temp2;
**Note :
-->The system datafile cannot be drop,cannot rename, and offline
-->cannot rename ,drop the sysaux datafile.
sys>>alter tablespace ts1 rename to ts2;
Rename the datafile
sys>>ALTER TABLESPACE ts2
RENAME DATAFILE '/u02/oracle/rbdb1/user1.dbf',
'/u02/oracle/rbdb1/user2.dbf'
TO '/u02/oracle/rbdb1/users01.dbf',
'/u02/oracle/rbdb1/users02.dbf';
To make the default tablespace for a datafile
sys>> alter database default tablespace ts2;
sys>>select * from database_properties;
sys>>alter dabase default temporary tablespace temp1;
Rename a temporary tablespace:
sys>>alter tablespace temp1 rename to temp2;
**Note :
-->The system datafile cannot be drop,cannot rename, and offline
-->cannot rename ,drop the sysaux datafile.
No comments:
Post a Comment